Publications
You can also find my articles on Google Scholar.
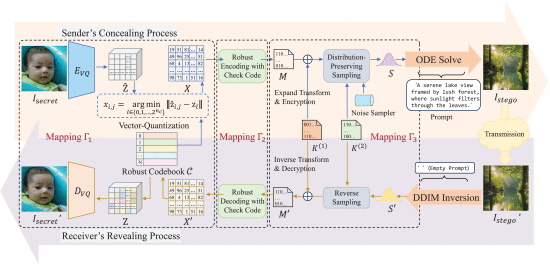
Robust Generative Steganography for Image Hiding Using Concatenated Mappings
Generative steganography stands as a promising technique for information hiding, primarily due to its remarkable resistance to steganalysis detection. Despite its potential, hiding a secret image using existing generative steganographic models remains a challenge, especially in lossy or noisy communication channels. This paper proposes a robust generative steganography model for hiding full-size image. It lies on three reversible concatenated mappings proposed. The first mapping uses VQGAN with an order-preserving codebook to compress an image into a more concise representation. The second mapping incorporates error correction to further convert the representation into a robust binary representation. The third mapping devises a distribution-preserving sampling mapping that transforms the binary representation into the latent representation. This latent representation is then used as input for a text-to-image Diffusion model, which generates the final stego image. Experimental results show that our proposed scheme can freely customize the stego image content. Moreover, it simultaneously attains high stego and recovery image quality, high robustness, and provable security.
show all ▼
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025
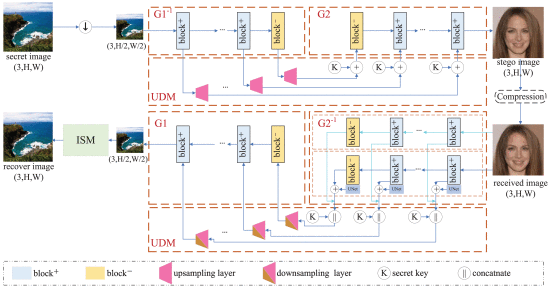
JPEG Compression-Resistant Generative Image Hiding Utilizing Cascaded Invertible Networks
Generative steganography is renowned for its exceptional undetectability. However, prevalent generative methods often have insufficient capacity for concealing secret images. Furthermore, the sensitivity of commonly utilized generative models exacerbates the challenge of ensuring robustness against channel distortions such as JPEG compression. In this paper, we introduce a generative image hiding network that employs two invertible generators to transform secret images into stego images within a disparate image domain. Additionally, we seamlessly integrate an up-and-down sampling module (UDM) within these generators to facilitate efficient decoupling of the intermediate representations obtained by each generator. The UDM serves multiple purposes: preserving coherence between the intermediate representations, enhancing resilience against JPEG compression, and safeguarding the confidentiality of the concealed images. To address the complexity of mapping both uncompressed and compressed stego images to a unified intermediary representation, we implement two distinct flows for the forward and backward processes of the generator associated with the stego images. The experimental results show that our scheme offers concurrent advantages in terms of full-size image hiding ability, undetectability, confidentiality, and robustness.
show all ▼
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025
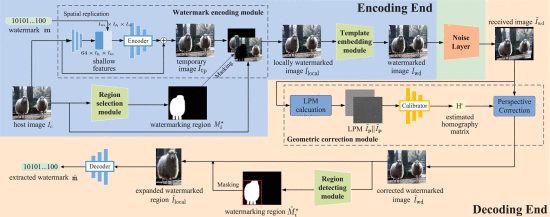
Camera-shooting resilient watermarking on image instance level
Capturing displayed images using portable cameras has become familiar among multimedia pirates, necessitating the urgent requirement of camera-shooting resilient watermarking schemes. In this paper, we consider the stealers who only record parts of images, and propose a robust watermarking scheme at the image instance level. This scheme consists of an encoding end, a noise layer, and a decoding end. The encoding end first selects specific watermarking regions associated with segmented image instances. Afterwards, an encoder is employed to embed watermark sequences into the RGB color model of these watermarking regions. At last, templates are embedded to product the final watermarked images. Specifically, our suggested template-based resynchronization comprises a template embedding module at the encoding end and a geometric correction module at the decoding end. The former embeds templates by a correlation-aware multiplicative spread spectrum with an adaptive amplitude, while the latter learns a calibrator to estimate the perspective projection. Experiments on both simulation and real-world scenarios support that the proposed scheme effectively resists camera-shooting attacks with various shooting conditions, regardless of whether the entire displayed images have been captured.
show all ▼
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024
Removing Hidden Information by Geometrical Perturbation in Frequency Domain
The risk of malicious exploitation of advanced image steganography necessitates the removal of hidden information from images. However, it is crucial to preserve the visual quality of the images undergoing processed. This paper suggests a geometrical attack in frequency domain (GAF) to address this challenge. GAF employs a thin plate spline (TPS) to slightly geometrically perturb the frequency components of the stego image. It incorporates a channel weight estimator and a frequency jammer. The channel weight estimator assigns perturbation strengths to each DCT channel, while the frequency jammer performs the TPS transform on the DCT channels using the assigned perturbation strengths. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach effectively hinders secret image recovery with a little distortion to the stego images. Furthermore, it well preserves the visual quality of clear images that do not contain secret information.
show all ▼
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024
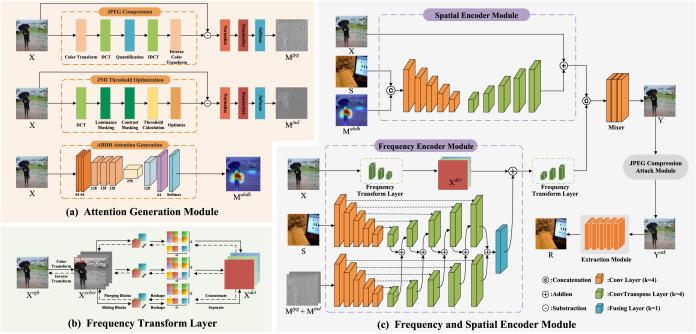
Robust image hiding network with Frequency and Spatial Attentions
Convert Image Communication (CIC) is a promising technology to protect the privacy of images. Recently, the emergence of robust CIC resistant to JPEG compression has gained due to the widespread use of JPEG compression in image communication. This paper introduces a Robust image hiding network with Frequency and Spatial Attentions (RFSA) to implement robust CIC. RFSA can hide an image within another image with high robust. It incorporates multiple image attentions corresponding to imperceptibility, recovered image quality, and resistance to JPEG compression, which ensure that secret images are hidden within regions that cause little distortion and can well withstand JPEG compression. Additionally, two encoders, that is, a frequency encoder and a spatial encoder, are mixed to adaptively embed secret images across both frequency and spatial domains. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed scheme not only maintains high image quality and capacity but also exhibits exceptional resistance to JPEG compression compared to other state-of-the-art image hiding methods. The average Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) of the recovered image remains at 24.96 dB even under JPEG compression with a quality factor of 55.
show all ▼
Pattern Recognition, 2024
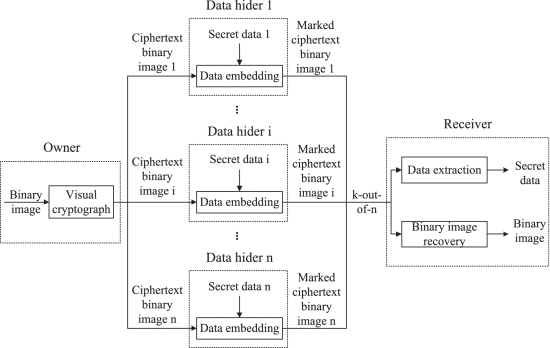
Multi-Party Reversible Data Hiding in Ciphertext Binary Images Based on Visual Cryptography
Existing methods for reversible data hiding in ciphertext binary images only involve one data hider to perform data embedding. When the data hider is attacked, the original binary image cannot be perfectly reconstructed. To this end, this letter proposes multi-party reversible data hiding in ciphertext binary images (MRDHCBI), where multiple data hiders are involved in data embedding. In this solution, we use visual cryptography technology to encrypt a binary image into multiple ciphertext binary images, and transmit the ciphertext binary images to different data hiders. Each data hider can embed data into a ciphertext binary image and generate a marked ciphertext binary image. The original binary image is perfectly reconstructed by collecting a portion of marked ciphertext binary images from the unattacked data hiders. Compared with existing solutions, the proposed solution enhances the recoverability of the original binary image. Besides, the proposed solution maintains a stable embedding capacity for different categories of images.
show all ▼
IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2025
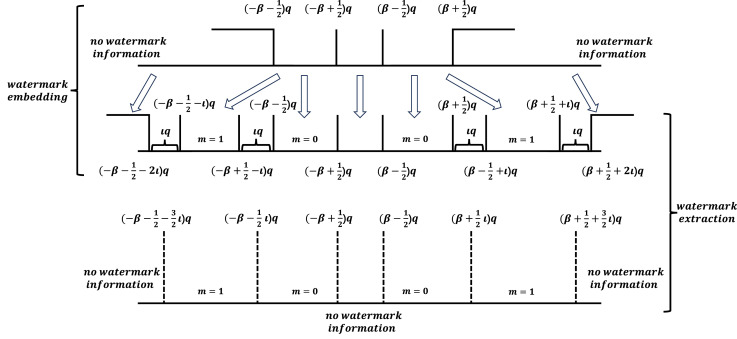
A robust reversible watermarking scheme using DC prediction and histogram shifting
Robust Reversible Watermarking (RRW) not only ensures the resilience of watermarked images under various attacks but also enables the exact recovery of the original host images from these watermarked versions. However, many existing RRW methods suffer from compromised reversibility when subjected to attacks, preventing successful restoration of the host image. In this paper, we explore the dual robustness of RRW—simultaneously enhancing both watermark resilience and reversibility. We propose a JPEG compression-resistant histogram-shifting algorithm that withstands targeted compression and exhibits strong robustness against common image manipulations. Building on this algorithm, we introduce two RRW schemes: one embeds watermark bits into the AC coefficients, and the other embeds them into the prediction error of DC coefficients. Furthermore, we design a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based DC predictor to infer DC coefficients from AC coefficients. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves superior robustness and watermarked image quality, while reliably preserving reversibility under various distortions.
show all ▼
Signal Processing, 2025
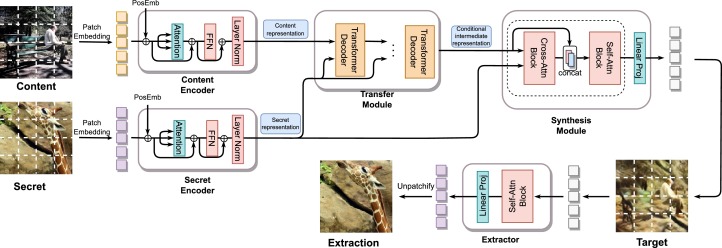
Conditional image hiding network based on style transfer
Various data hiding methods have been suggested to hide secret images within stego images. However, many of them could be easily detected by steganalytic tools due to their large hidden information. In this paper, we enhance the undetectability of image hiding network by mapping latent representation conditional on secret information. We extend the idea of image generation-based steganography and propose a Transformer-based image hiding network, which can hide secret images of the same size as the target image. The proposed scheme uses style transfer to help map the latent representation. The proposed scheme's hiding network includes three modules: encoding module, transfer module, and synthesis module. The encoding module extracts latent representations from the content image and the secret image, the transfer module stylizes intermediate representations conditional on secret information, and the synthesis module fuses the stylized features and the secret image features to synthesize the target image with the secret image hidden in it. A new synthesis module and corresponding extraction network are developed to improve recovery accuracy. The proposed scheme shows high image quality on both target images and recovered secret images. Furthermore, it is robust to steganalytic tools, thus providing good security.
show all ▼
Information Sciences, 2024
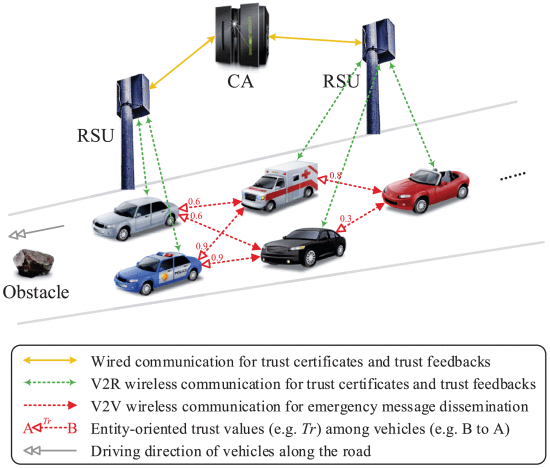
TCEMD: A Trust Cascading-Based Emergency Message Dissemination Model in VANETs
Vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs) have recently attracted considerable attention from both industry and academia for improving road safety and traffic efficiency. Trust modeling plays a significant role in VANETs, however, the existing trust models cannot primely conform to the characteristics of VANETs. This article proposes a novel trust cascading-based emergency message dissemination (TCEMD) model which incorporates the entity-oriented trust values into data-oriented trust evaluation in an efficient manner. In the proposed model, when an emergency event (e.g., an obstacle in front of the road) occurs, the emergency messages can be disseminated among the nearby vehicles in a trust cascading manner, where the entity-oriented trust values (which are evaluated and updated by leveraging the trust certificates and are contained in the messages) are adopted as important weights. Subsequently, the theoretical analysis for the robustness against several kinds of attacks and malicious behaviors, failure tolerance features, compatibility for several kinds of special situations, and incentive mechanisms in the TCEMD model are detailed. Afterwards, a series of simulations and analyses are conducted in a typical highway environment, and the results reveal that the proposed model significantly outperforms the existing models in several cases.
show all ▼
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019